Remote Sensing
The Problem
How do we find and characterize GHG emissions over vast geographic regions?
Butterfly’s Approach
Use the sun as a light source to spectroscopically probe the atmospheric column
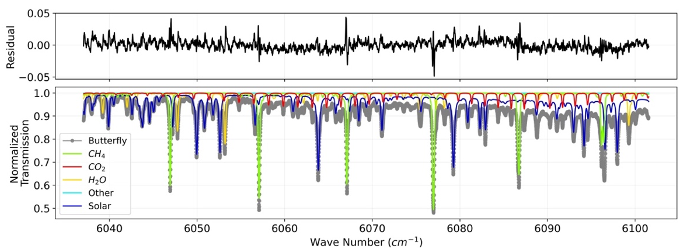
Typical column spectrum observed using a Butterfly spectrometer. Molecular absorptions due to methane, CO2 and water are clearly observed and processed using CalTech’s GGG analysis suite.
Basin-Wide Deployment
With several autonomous sensors strategically placed, the total column abundances of methane, CO2 and water vapor can be measured throughout the day (as long as the sun is shining). The data is interpreted using sophisticated transport models to produce time-dependent maps of these critical GHGs.